We are starting a whole new topic on lipids now.
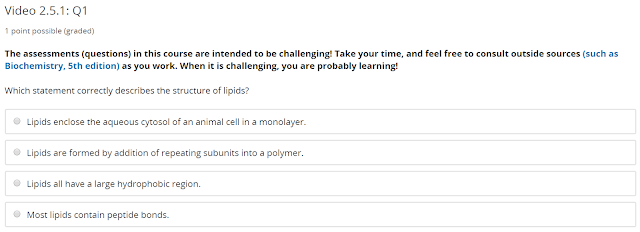
Lipids encloses aqueous cytosol of an animal cell in a bilayer (not a monolayer) - the monolayer is used to enclose triacylglycerols in adipocytes.
Lipids are not polymers.
Sphingolipid have peptide bonds, but most other don't.
Therefore the correct answer is:
Lipids all have a large hydrophobic region.
Sphingosine has a amine group, not a nitrogen group. I don't know if the term "nitrogen group" exists or not, the closest I can think of is cyanide, which is highly toxic.
The molecule drawn has a double bond in it, so it is not saturated.
Lipid formed with sphingosine, such as sphingomyelin, are often structural lipid, not storage lipid.
Therefore the correct answers are:
Sphingosine already contains one hydrocarbon 'tail', and
Sphingosine serves as a backbond, like glycerol.
Each of the 3 hydroxyl group of glycerol and the carboxylic acid group of the fatty acid reacts to form ester bonds, that's how triacylglycerols are formed. Therefore, the correct answer is:
... a fatty acid is esterified to each hydroxyl group of glycerol.
The key intermolecular interaction force between lipid molecules is Van der Waal's force. Molecule A, a saturated lipid is more regular and can be closely packed, therefore it will have more Van der Waal's force. On the other hand, molecule B will have less and therefore easier to boil, and theerfore it is more likely to be liquid at room temperature.
Lipids encloses aqueous cytosol of an animal cell in a bilayer (not a monolayer) - the monolayer is used to enclose triacylglycerols in adipocytes.
Lipids are not polymers.
Sphingolipid have peptide bonds, but most other don't.
Therefore the correct answer is:
Lipids all have a large hydrophobic region.
Sphingosine has a amine group, not a nitrogen group. I don't know if the term "nitrogen group" exists or not, the closest I can think of is cyanide, which is highly toxic.
The molecule drawn has a double bond in it, so it is not saturated.
Lipid formed with sphingosine, such as sphingomyelin, are often structural lipid, not storage lipid.
Therefore the correct answers are:
Sphingosine already contains one hydrocarbon 'tail', and
Sphingosine serves as a backbond, like glycerol.
Each of the 3 hydroxyl group of glycerol and the carboxylic acid group of the fatty acid reacts to form ester bonds, that's how triacylglycerols are formed. Therefore, the correct answer is:
... a fatty acid is esterified to each hydroxyl group of glycerol.
The key intermolecular interaction force between lipid molecules is Van der Waal's force. Molecule A, a saturated lipid is more regular and can be closely packed, therefore it will have more Van der Waal's force. On the other hand, molecule B will have less and therefore easier to boil, and theerfore it is more likely to be liquid at room temperature.



No comments:
Post a Comment